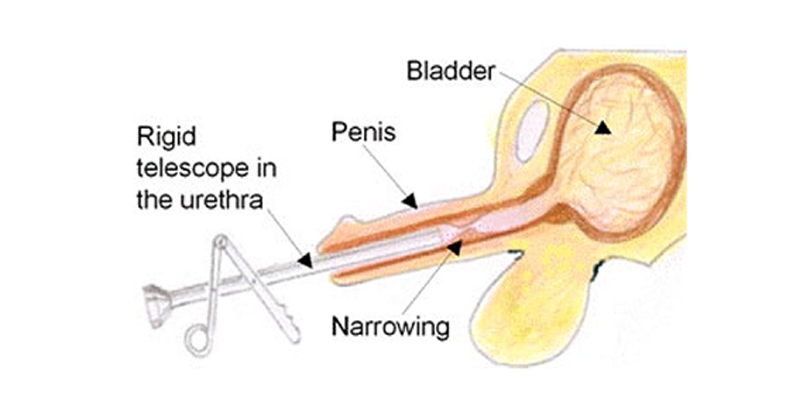
Overview
A urethral (u-REE-thrul) stricture involves scarring that narrows the tube that carries urine out of your body (urethra). A stricture restricts the flow of urine from the bladder and can cause a variety of medical problems in the urinary tract, including inflammation or infection.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of urethral stricture include:
- Decreased urine stream
- Incomplete bladder emptying
- Spraying of the urine stream
- Difficulty, straining or pain when urinating
- Increased urge to urinate or more-frequent urination
- Urinary tract infection
Causes
Scar tissue, which can narrow the urethra, can be due to:
- A medical procedure that involves inserting an instrument, such as an endoscope, into the urethra
- Intermittent or long-term use of a tube inserted through the urethra to drain the bladder (catheter)
- Trauma or injury to the urethra or pelvis
- An enlarged prostate or previous surgery to remove or reduce an enlarged prostate gland
- Cancer of the urethra or prostate
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Radiation therapy
Urethral stricture is much more common in males than in females. Often the cause is unknown.
