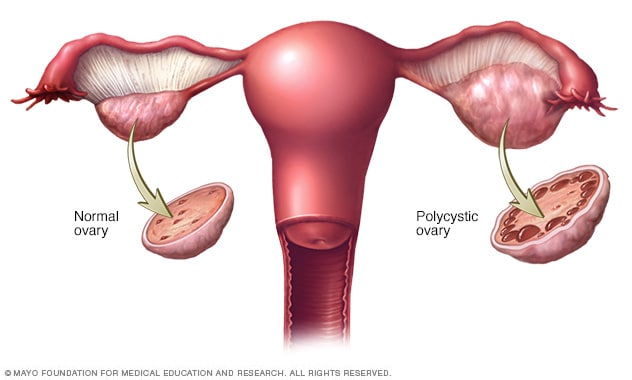
PCOS is a hormonal disorder which is common among young females of reproductive age. This condition is also known as“STEIN-LEVANTHAL SYNDROME” or “HYPERANDROGENIC ANOVULATION”. Polycystic primarily means ‘many cysts’ and cysts are filled with fluid and immature cysts.
CAUSES:
The exact cause of PCOS is not clear but there are some factors that play a role in causing Polycystic ovaries. These factors are as follows;
- Insulin excess due to insulin resistance. Excess insulin might increase androgen production causing difficulty in ovulation.
- Low-grade inflammation is seen in women with PCOS, that stimulates polycystic ovaries to produce androgen which can lead to heart and blood vessels problems.
- The genetic factor is one of the reasons behind PCOS.
- Excess production of androgens from the ovaries and adrenals occurs due to abnormal regulation of the androgen forming enzyme.
CLINICAL FEATURES:
PCOS is manifested mainly by menstrual abnormalities in form of oligomenorrhoea, amenorrhea or DUB; hirsutism; obesity along with enlarged polycystic ovaries. If left Untreated, it can lead to infertility. This complex disorder is characterized by excessive androgen production by the ovaries and adrenals which interferes with the growth of the ovarian follicles. Therefore, PCOS is a state of androgen excess and chronic anovulation.
Acanthosis nigricans is characterized by specific skin changes due to insulin resistance. Skin becomes thickened and pigmented.
Apart from above-mentioned symptoms, PCOS also manifest itself by sleep apnea, high-stress level, hypertension, skin tags, acne, oily skin, dandruff, high cholesterol and triglycerides, fatigue, male pattern baldness, type 2 diabetes, pelvic pain, depression, anxiety, and decreased libido.
TEST AND DIAGNOSIS:
No single test can determine the presence of PCOS but some tests are helpful in making the diagnosis along with a detailed medical history of the patient.
- Blood test to assess the serum values of LH, LH/FSH ratio, oestrone level, androstenedione level, serum testosterone, and DHEA-S. All values are elevated if PCOS is present.
- Serum insulin level (insulin resistance) ratio of fasting glucose: fasting insulin is <4.5.
- Lipid profile- cholesterol and triglycerides level are elevated in case of developed PCOS.
- Sonography shows enlarged ovaries with the increased number of peripherally arranged cysts. In case of obese patients, a transvaginal ultrasound is specially useful.
- Laparoscopy shows bilateral polycystic ovaries.
TREATMENT:
Some of the best homeopathic remedies that are found helpful in treating PCOS are as follows;
Sepia–
- irregular menses of nearly every form; early, late, scanty, profuse.
- Amenorrhea or menorrhagia
- Anxiety with fear
- Great falling of the hair
- Great sadness and weeping
- Pot- belliedness of mothers
Pulsatilla–
- scanty or protracted menstruation
- Delayed first menstruation
- Inclined to be fleshy
- Intense pain with restlessness
- Weeps easily
Calcarea carb –
- menstruation too early, too profuse, too long lasting
- Subsequent amenorrhea and chlorosis with scanty menses or suppressed
- Least mental excitement causes profuse return of menstrual flow.
- Disposed to grow fat
Natrum Mur –
- profuse menses or irregular menstruation
- Sad weeping mood without cause
- Hair fall on slight touch
- retarded menstrual flow
- Distressing and burning pain in left ovarian region
- Hair dry and falling out
Homeopathy is the only system that looks at the whole person and just at their hormones and ovaries.
